定时任务
这篇文档介绍了如何在 Linux 下设定定时任务,这是开发运维中经常要做的事情。很多老的文档,仍然使用 Crontab 来设定定时任务。但是随着新版的 Debian、Ubuntu 以及 CentOS 的发布,建议使用 Systemd Timers 来替代 Crontab。
示例
比如说,我要写一个定时任务,对某个 Docker 容器做健康检查,每分钟执行一次,如果检查失败则重启容器。步骤如下:
首先,需要创建一个 timer 类型的文件,我取名为 health-check.timer, 执行命令 vim /etc/systemd/system/health-check.timer, 写入如下内容:
接着,创建一个 service 类型的文件,文件名必须和上文创建的 timer 文件一样,执行命令vim /etc/systemd/system/health-check.service, 写入如下内容:
最后,我们启用并启动 timer 任务。下面的命令首先重新加载了 Systemd 守护进程来识别你的新服务和定时器。然后它启动定时器,并且确保在重启之后定时器是被激活的。
查看 Timer 的状态,示例如下:
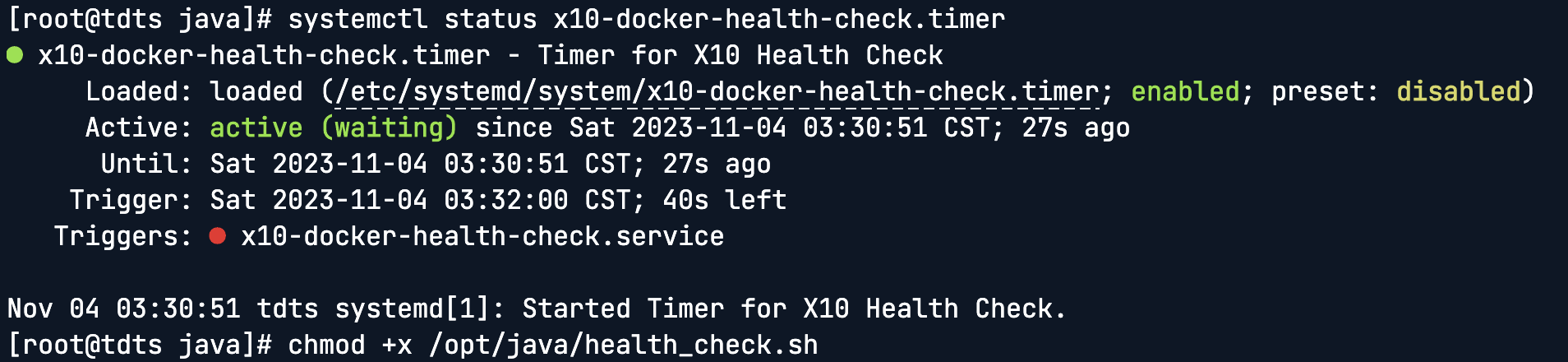
查看启用的定时任务, 示例如下:
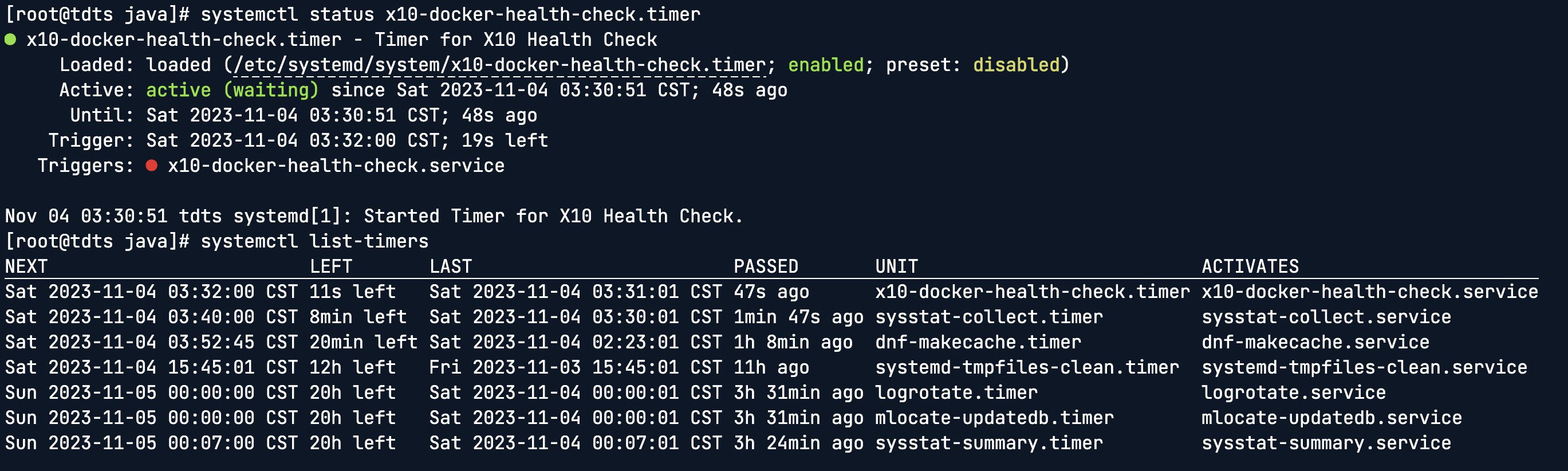
Systemd Timers 的优点
集成性 :Systemd timers 是 Systemd 的一部分,它和 Systemd 的其他部分(如服务管理)有很好的集成。
灵活性 :Systemd timers 提供了更多的触发条件和更复杂的时间安排选项。
日志和状态 :Systemd 提供了内置的状态和日志记录工具,可以直接查看服务的状态和日志输出。
依赖管理 :Systemd timers 可以利用 Systemd 的依赖关系和顺序来精确控制服务的启动和停止。
总结
这篇文档介绍了如何使用 Systemd timers 来创建定时任务,并且介绍了相对于历史悠久的 Crontab 的优势。